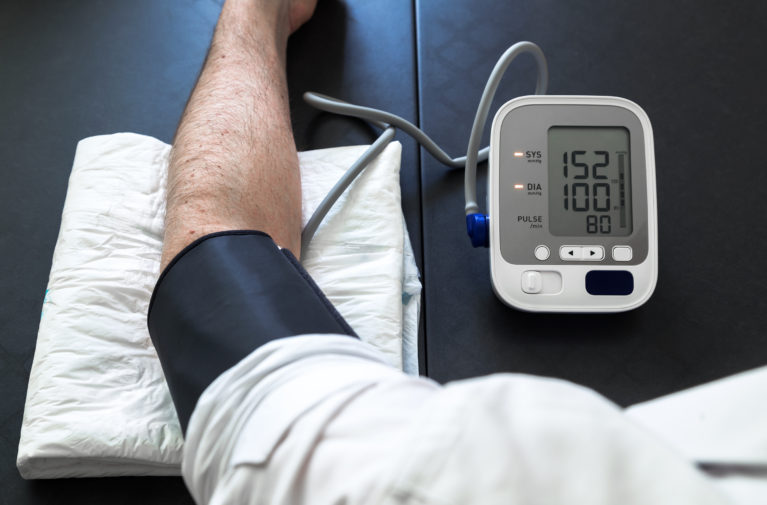
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common medical condition characterized by the increase in the pressure against the inner walls of the arteries as blood moves through them. Obesity, another common but serious condition, has been shown to increase the risk of developing hypertension significantly. How does obesity cause hypertension and how can weight loss help?
The Relationship Between Obesity and Hypertension
An excess of fatty tissue in the body puts extra pressure on the body’s internal systems, which increases vascular resistance (a force that must be overcome to push blood through the body’s circulatory system). The greater the resistance, the harder the heart must work to pump blood through the body.
How Weight Loss Impacts a Hypertensive Body
Weight loss is the single most critical step to lowering blood pressure in overweight individuals. It lightens the load on the heart to move blood throughout the circulatory system, and losing as little as five to ten pounds can result in a noticeable drop and systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings. Weight loss also reduces the risk of other diseases associated with obesity and hypertension, such as diabetes and coronary heart disease.
How Hypertensive People Can Lose Weight
Weight loss is never easy, but it’s important for individuals who have hypertension or who are overweight to take a calculated approach to shed pounds. Unhealthy weight loss, like pounds that melt away too quickly or crash dieting, can cause additional problems for people who also have medical conditions that affect the heart. Here’s how you can lose weight safely if you are overweight and have hypertension:
- Consult a Physician – Before starting any diet or exercise program, you need to make sure it’s safe for you to do so. Most of the time, it’s a resounding “yes,” however, you may need to modify what exercises you do or how many calories you need to eat to gradually ease your body into the new routines. Make an appointment with a physician to establish a baseline for your blood pressure, blood sugar, and weight, and to get the green light to start safely.
- Eat a Hypertension-Friendly Diet – A hypertension-friendly diet focuses on reducing caloric intake to facilitate fat burn, but also restricts saturated fats and sodium, both things that can cause an increase in blood pressure. The DASH diet, which is sponsored by the U.S. National Institutes of Health, follows basic guidelines for sodium and cholesterol. However, it focuses on incorporating whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and other fresh foods and switching to low or no-fat dairy. The DASH diet is also recommended by the American Heart Association, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, and the Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
- Engage in Safe Exercise – Exercise is another important part of healthy weight loss. Weight loss is essentially math; it occurs any time that calorie output is greater than calorie input. It’s often very difficult to restrict the diet enough to bring caloric intake below the threshold that weight loss occurs alone. When caloric intake is reduced and output is increased through exercise, it becomes easier to see weight loss without cutting down the intake of food beyond what is healthy.
Safe exercise is also important for overweight and obese individuals. Excess weight can change the body’s center of gravity, which can make it difficult to balance and can result in falls or injuries. It’s also crucial to ensure that the heart can withstand an increase in exercise. By checking with a physician, you can make sure you’re exercising in a way that is right for you.
About Dr. Edward Mallory
Dr. Edward Mallory is a physician and Florida medical expert witness that offers expert testimony in malpractice cases throughout the US. The necessity of medical expert witnesses is growing, and both high and low profile cases can benefit from the expertise of a seasoned medical witness to help judges and juries better understand complex medical concepts. Contact Dr. Mallory online or call now for a consultation at (813) 997-1241.